On Grid Solar Systems
In recent years, on grid solar systems have gained significant popularity as a sustainable and cost-effective solution for generating electricity. These systems are directly connected to the utility grid and play a vital role in the transition to cleaner energy sources.
Let’s delve into a detailed exploration of on-grid solar systems, covering their components, how they work, benefits, considerations, and their impact on the energy landscape.
Components of an On Grid Solar Systems
- Solar Panels: At the heart of an on-grid solar system are solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) modules. These panels are made up of silicon cells that convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
- Inverter: Solar panels produce direct current (DC) electricity, but homes and businesses use alternating current (AC) electricity. The inverter is a crucial component that converts DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity suitable for powering electrical devices.
- Mounting Structure: Solar panels are typically mounted on rooftops or ground-mounted structures to maximize sunlight exposure. The mounting structure ensures the panels are securely installed and positioned for optimal solar energy capture.
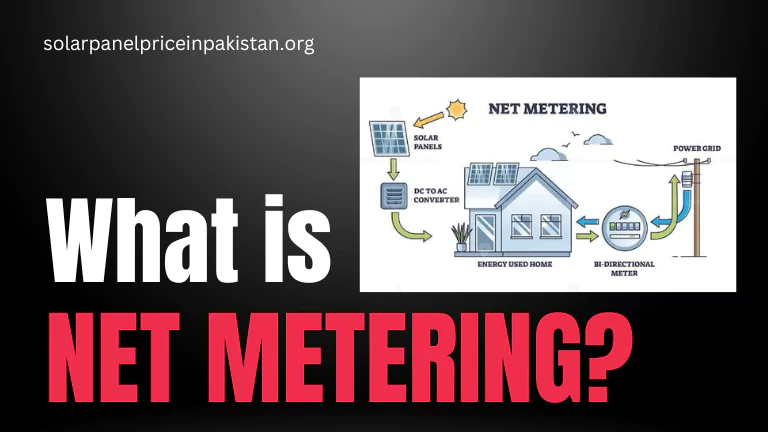
- Bi-Directional Meter: An essential part of an on-grid system is the bi-directional meter. This meter measures the electricity flow between the solar system and the utility grid, allowing for accurate monitoring of energy production and consumption.
- Grid Connection: On-grid solar systems are connected to the utility grid through electrical wiring. This connection enables the seamless exchange of electricity between the solar system and the grid as needed.
How On Grid Solar Systems Work?
- Solar Energy Generation: During daylight hours, solar panels harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. The intensity of sunlight directly impacts the amount of electricity generated by the panels.
- Inverter Conversion: The DC electricity produced by solar panels is sent to the inverter, where it undergoes conversion into AC electricity. This AC electricity is then used to power appliances, lights, and other electrical devices in homes or businesses.
- Grid Interaction: Excess electricity generated by the solar system that is not immediately consumed on-site is fed back into the utility grid. This surplus electricity flows through the bi-directional meter, and depending on local regulations and policies, homeowners or businesses may receive credits or compensation for the exported electricity.
- Grid Usage: When solar energy production is insufficient to meet on-site demand, electricity is drawn from the utility grid as usual. This ensures a continuous and reliable power supply, especially during periods of low sunlight or at night.
Benefits of On Grid Solar Systems
- Cost Savings: On-grid solar system can significantly reduce electricity bills by offsetting or eliminating the need to purchase electricity from the grid. Excess electricity exported to the grid may also result in financial credits or payments.
- Environmental Impact: By utilizing clean and renewable solar energy, on-grid system help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to a greener and more sustainable environment.
- Financial Incentives: Many regions offer incentives such as tax credits, rebates, or feed-in tariffs for installing on-grid solar systems, making them financially attractive and accelerating their adoption.
- Grid Stability: On-grid solar systems contribute to the stability and resilience of the utility grid by diversifying energy sources, reducing strain during peak demand periods, and enhancing overall grid reliability.
- Energy Independence: While connected to the grid, on-grid solar systems provide a degree of energy independence and security against rising electricity costs, offering homeowners and businesses greater control over their energy usage and expenses.
Considerations for On-Grid Solar Systems
- Net Metering Policies: Understanding and leveraging net metering policies is crucial for maximizing the financial benefits of an on-grid solar system. Net metering allows homeowners or businesses to receive credits for excess electricity exported to the grid.
- System Sizing: Properly sizing an on-grid solar system involves assessing energy consumption patterns, available roof space or land for solar panels, desired energy production goals, and local regulatory requirements.
- Installation and Maintenance: Professional installation by certified solar installers ensures the system operates efficiently and safely. Regular maintenance, including cleaning panels and inspecting components, helps maximize system performance and longevity.
- Backup Power Options: On-grid solar systems typically do not provide backup power during grid outages. Consider integrating battery storage or backup generators if uninterrupted power supply is a priority.
The Role of On-Grid Solar in a Sustainable Future
On-grid solar systems play a vital role in the global shift towards clean, renewable energy sources and sustainable energy practices. Their widespread adoption contributes to reducing carbon emissions, mitigating climate change impacts, enhancing energy security, and fostering a more resilient and decentralized energy infrastructure.
As technology advances, costs decrease, and policies favor renewable energy, on-grid solar systems continue to empower individuals, communities, and businesses to embrace cleaner and more efficient energy solutions, ultimately paving the way for a greener and brighter future.
Check More: